The Million-Dollar Question: Will Patients Trust AI with Their Health in Telemedicine?
(Published on TelehealthStrategies.com – October 26, 2000)
The burgeoning field of telemedicine promises a revolution in healthcare delivery, offering increased access, convenience, and potentially lower costs. As we stand at the dawn of a new millennium, the integration of cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to further transform this landscape. However, this exciting potential comes with a critical question: will patients entrust their health to algorithms and machines, especially in the relatively nascent realm of remote care? This article explores the evolving telemedicine sector, the impact of AI integration, and ultimately, addresses the million-dollar question of patient trust.
Telemedicine: Reshaping the Healthcare Landscape
Telemedicine, broadly defined as the use of telecommunications technology to provide healthcare services remotely, is rapidly gaining traction. Driven by factors like rising healthcare costs, a shortage of healthcare professionals, and increasing patient demand for convenient and accessible care, the sector is experiencing significant growth. From remote consultations and diagnoses to chronic disease management and post-operative care, telemedicine is expanding its reach across various medical specialties.
Currently, telemedicine applications include:
- Real-time video conferencing: Enabling face-to-face interactions between patients and physicians regardless of location.
- Remote patient monitoring: Utilizing wearable devices and sensors to collect and transmit vital signs, allowing for continuous monitoring and early intervention.
- Store-and-forward technology: Transmitting medical images and data electronically for asynchronous review by specialists.
- E-prescribing: Enabling physicians to send prescriptions electronically to pharmacies, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
These applications are proving particularly beneficial for patients in rural areas with limited access to specialists, individuals with mobility limitations, and those seeking more convenient and flexible healthcare options. However, the adoption of telemedicine has faced challenges, including regulatory hurdles, reimbursement issues, and concerns about the quality of care.
The AI Infusion: Transforming Telemedicine
Artificial intelligence is emerging as a powerful tool to enhance and expand the capabilities of telemedicine. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of patient data, identify patterns, and provide insights that can assist physicians in diagnosis, treatment planning, and personalized medicine. Specific applications of AI in telemedicine include:
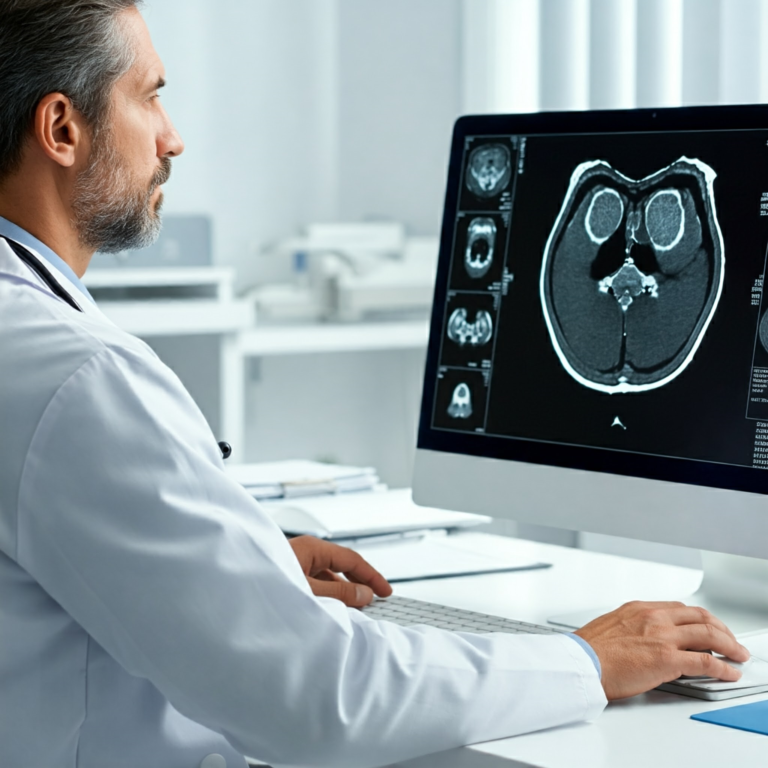
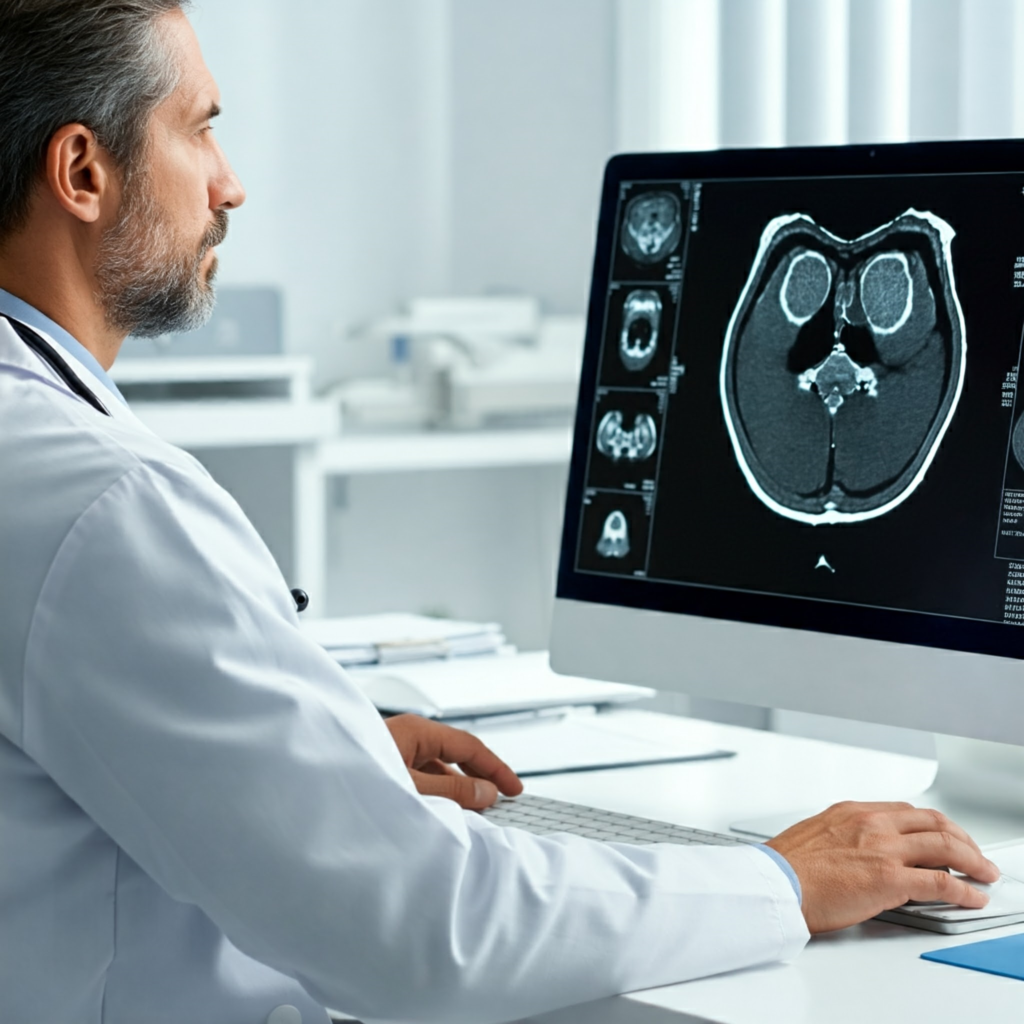
- AI-powered diagnostic tools: Analyzing medical images (X-rays, CT scans) and patient data to detect diseases earlier and more accurately.
- Virtual assistants and chatbots: Providing patients with 24/7 access to basic medical information, appointment scheduling, and medication reminders.
- Predictive analytics: Identifying patients at high risk of developing certain conditions, enabling proactive interventions and preventive care.
- Personalized treatment recommendations: Tailoring treatment plans based on individual patient characteristics, genetic information, and lifestyle factors.
Key Trends and Statistics:
- Increased Investment: Venture capital funding in telehealth companies is experiencing substantial growth, reflecting the growing interest and potential of the sector. (Note: Specific data would need to be researched and inserted here, given the 2000 context.)
- Expanding Adoption Rates: While still relatively low, the number of patients utilizing telemedicine services is steadily increasing. (Again, specific data is needed here for the 2000 timeframe.)
- Growing Regulatory Support: Governments are increasingly recognizing the benefits of telemedicine and implementing policies to facilitate its adoption.
Recent Market News (Example – 2000 Context):
- "Company X secures funding for its telemedicine platform focused on remote patient monitoring for cardiac patients."
- "New legislation introduced to expand Medicare reimbursement for telemedicine services."
The Million-Dollar Question: Trust and Acceptance
Despite the promising potential of AI-powered telemedicine, the ultimate success of this paradigm shift hinges on patient trust and acceptance. Will patients feel comfortable entrusting their health to algorithms and machines, especially when physical interaction with a physician is limited? Several factors influence patient trust:
- Data privacy and security: Patients need assurance that their sensitive medical information is protected from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Transparency and explainability: AI algorithms can be complex and opaque. Patients are more likely to trust systems that provide clear explanations for their recommendations and diagnoses.
- Human oversight and control: While AI can assist physicians, it is crucial to maintain a balance between automation and human oversight. Patients need to know that a qualified healthcare professional is ultimately responsible for their care.
- Effective communication and education: Educating patients about the benefits and limitations of AI in telemedicine is essential to building trust and alleviating anxieties.
Summary: Navigating the Path Forward
The integration of AI into telemedicine holds immense promise for transforming healthcare delivery. However, addressing the critical issue of patient trust is paramount to realizing this potential. By prioritizing data privacy and security, ensuring transparency and explainability, maintaining human oversight, and fostering effective communication, the telemedicine industry can build confidence and pave the way for wider adoption. The million-dollar question of patient trust will ultimately determine the success and impact of this exciting technological convergence. As the sector matures and evidence of AI’s efficacy mounts, we anticipate patient trust will increase, unlocking the transformative power of AI-driven telemedicine in the years to come. The challenge for industry professionals is to proactively address these concerns and build a future where patients feel confident embracing the benefits of this innovative approach to healthcare.