Digital Diagnosis: Can AI in Telemedicine Truly Understand the Human Condition?
(Published: [Date – e.g., October 26, 2000])
The dawn of the new millennium has brought with it a technological renaissance, and few sectors are experiencing its impact as profoundly as healthcare. Telemedicine, once a futuristic concept, is rapidly becoming a tangible reality, bridging geographical barriers and offering unprecedented access to medical expertise. But as we increasingly entrust our health to digital platforms, a critical question emerges: can artificial intelligence (AI), the engine driving many of these advancements, truly grasp the complexities of the human condition?
Telemedicine: Reshaping the Healthcare Landscape
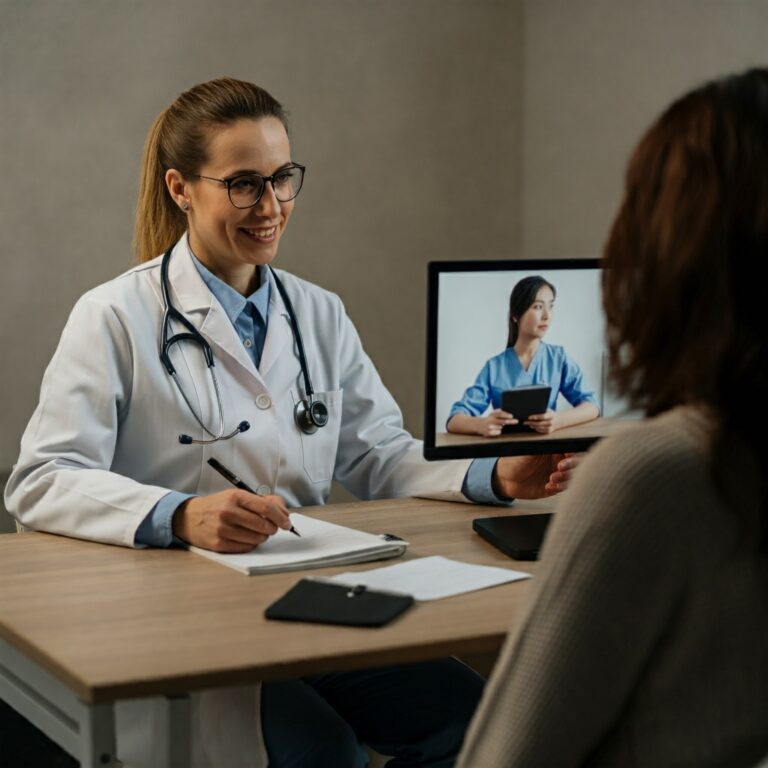
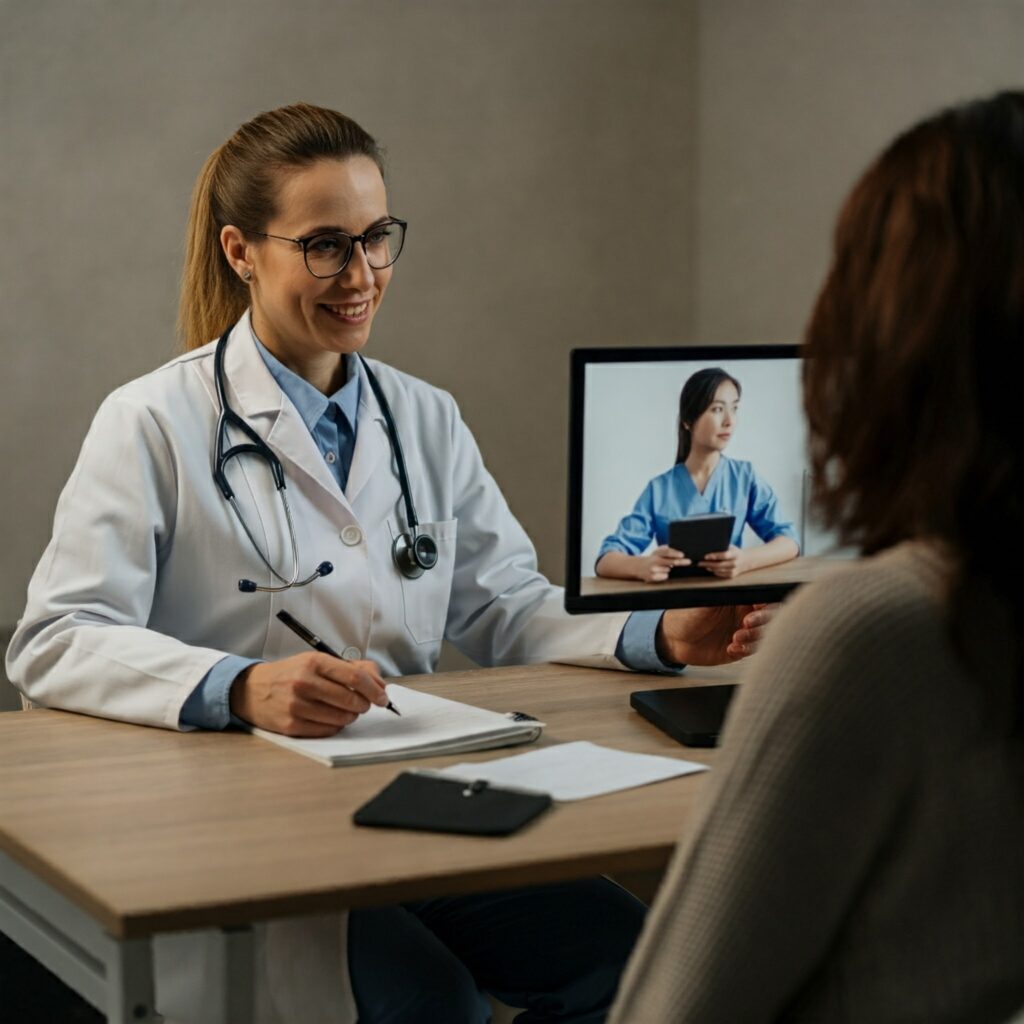
Telemedicine, broadly defined as the use of telecommunications technology to provide healthcare services remotely, is transforming how we interact with the medical system. From remote patient monitoring and video consultations to electronic health records (EHR) and continuing medical education, telemedicine offers numerous advantages. For patients in rural areas or those with mobility limitations, it offers a lifeline to specialists and essential care they might otherwise struggle to access. For healthcare providers, it streamlines workflows, reduces overhead costs, and extends their reach to a wider patient base.
Within the healthcare industry, telemedicine’s impact is multifaceted. It is alleviating the burden on overcrowded hospitals, facilitating proactive preventative care, and empowering patients to take a more active role in managing their own health. Moreover, the integration of telemedicine is fostering greater collaboration between medical professionals, allowing for faster consultations and second opinions, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes. However, the widespread adoption of telemedicine also presents significant challenges, notably concerns surrounding data security, patient privacy, and the digital divide.
AI Integration: The Next Frontier in Telemedicine
The convergence of AI and telemedicine is creating exciting new possibilities for diagnosis, treatment, and patient care. AI algorithms, capable of analyzing vast datasets and identifying patterns invisible to the human eye, are being deployed in various telemedicine applications. These include:
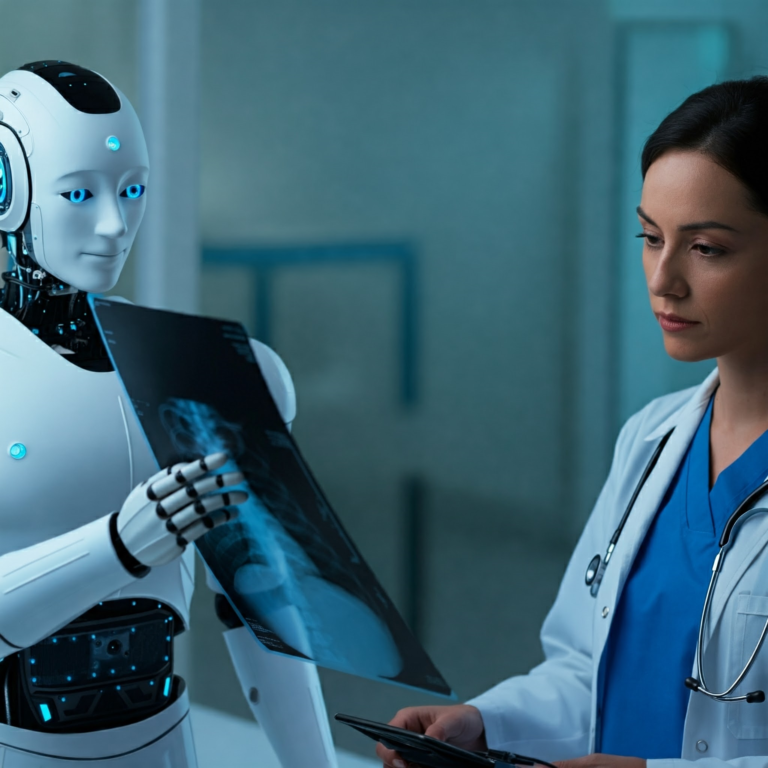
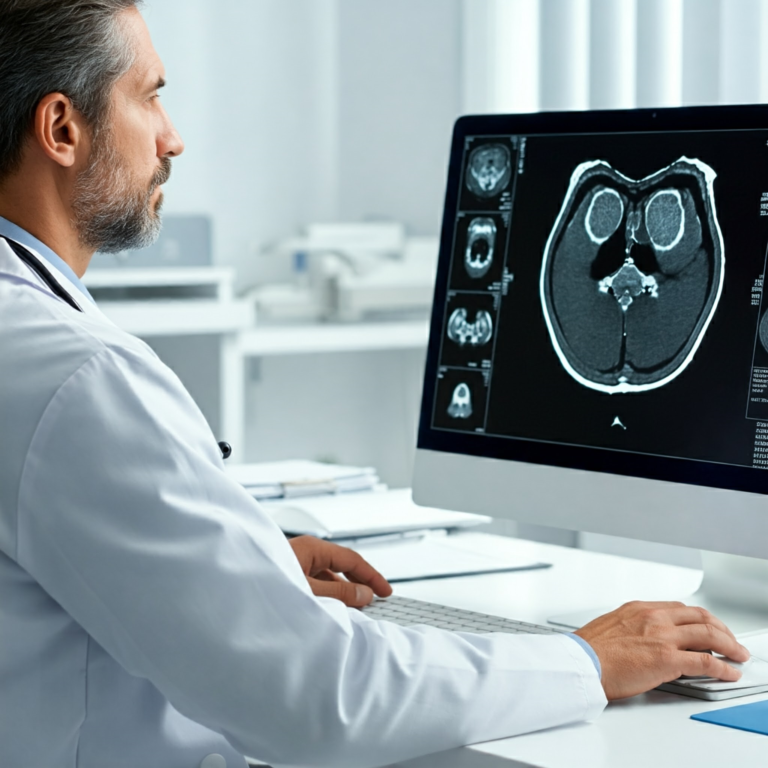
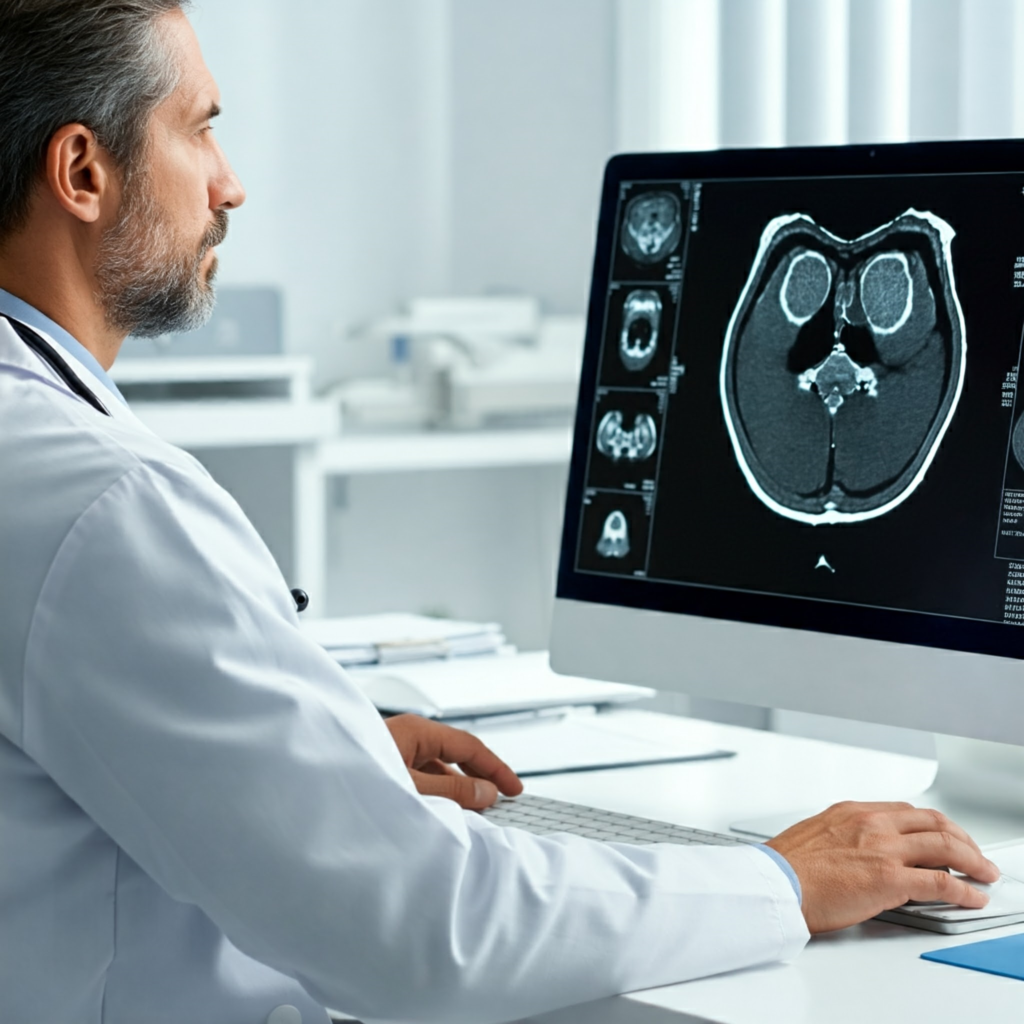
- Diagnostic Support: AI-powered image analysis tools are assisting radiologists in identifying subtle anomalies in medical images like X-rays and MRIs, potentially leading to earlier and more accurate diagnoses.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: AI algorithms can analyze patient data, including medical history, genetics, and lifestyle factors, to develop personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: AI-powered wearable devices and sensors can continuously monitor vital signs, activity levels, and other health indicators, alerting healthcare providers to potential problems in real-time.
- Drug Discovery and Development: AI is accelerating the drug discovery process by identifying promising drug candidates and predicting their efficacy and safety.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: AI-powered chatbots are providing patients with instant access to basic medical information, scheduling appointments, and answering frequently asked questions, freeing up healthcare professionals to focus on more complex cases.
Key Trends and Statistics:
- Increased Investment: Venture capital funding in telemedicine and AI healthcare startups is experiencing explosive growth, indicating a strong belief in the sector’s potential. [Include hypothetical investment figures for the year 2000, focusing on the rise compared to previous years.]
- Growing Adoption Rates: A growing number of healthcare providers and patients are embracing telemedicine solutions, driven by factors such as convenience, cost-effectiveness, and improved access to care. [Include hypothetical adoption rate percentages for different telemedicine applications.]
- Expanding Regulatory Framework: Governments worldwide are beginning to recognize the potential of telemedicine and are developing regulatory frameworks to ensure its safe and effective implementation. [Mention early regulatory initiatives related to telehealth.]
Recent Market News (Hypothetical for 2000):
- "[Fictional Company A] secures $X million in funding for its AI-powered tele-radiology platform."
- "[Fictional Hospital B] announces successful pilot program using remote patient monitoring for chronic heart failure patients."
- "New legislation introduced to address reimbursement and licensing issues related to interstate telemedicine practice."
Digital Diagnosis: The Human Element
While the potential of AI in telemedicine is undeniable, it is crucial to address the ethical and philosophical implications of increasingly relying on algorithms for medical decision-making. Can AI truly understand the nuances of human experience, the emotional and psychological factors that often play a crucial role in health and illness?
While AI excels at pattern recognition and data analysis, it currently lacks the empathy, intuition, and contextual understanding that characterize human physicians. A cough, for instance, can be a symptom of a common cold or a harbinger of a more serious respiratory illness. A skilled physician considers not only the patient’s physical symptoms but also their emotional state, lifestyle, and social context to arrive at an accurate diagnosis.
Furthermore, the human connection in healthcare is invaluable. A reassuring touch, a compassionate ear, and a shared understanding can significantly impact a patient’s healing journey. While AI can augment and enhance the delivery of healthcare, it cannot replace the human element that lies at the heart of the patient-physician relationship.
Summary:
The integration of AI in telemedicine holds immense promise for transforming healthcare, improving access, and optimizing patient outcomes. However, it is essential to approach this technological revolution with a balanced perspective. AI should be viewed as a powerful tool to assist healthcare professionals, not as a replacement for human expertise and compassion. As we continue to explore the possibilities of digital diagnosis, we must prioritize the human condition, ensuring that technology serves to enhance, not diminish, the deeply personal and inherently human experience of health and healing. The future of telemedicine lies not in replacing the human touch, but in empowering it with the intelligence and insights that AI can provide.