The Future of Remote Care: AI’s Promise and Peril in Telehealth
(Published on [Website Name], [Date in Year 2000 format, e.g., October 26, 2000])
The dawn of the new millennium has brought with it a technological renaissance, impacting nearly every facet of our lives. Healthcare, a sector traditionally resistant to rapid change, is now experiencing a seismic shift fueled by the convergence of computing power, internet connectivity, and innovative thinking. At the heart of this transformation lies telemedicine, a burgeoning field promising to revolutionize how healthcare is delivered and accessed. Within this rapidly evolving landscape, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is emerging as a powerful force, offering both immense promise and potential peril. This article delves into the evolving role of AI in telehealth, exploring its impact, key trends, recent market news, and ultimately, its implications for the future of remote care.
Telemedicine: Reshaping the Healthcare Landscape
Telemedicine, the practice of delivering healthcare services remotely using telecommunications technology, is no longer a futuristic concept. It’s a tangible reality transforming how patients interact with healthcare providers. From video consultations and remote patient monitoring to electronic health records (EHRs) and online prescription renewals, telemedicine offers increased access, convenience, and cost-effectiveness. This is particularly significant for patients in rural areas, those with mobility limitations, and individuals managing chronic conditions.
The drivers behind telemedicine’s growth are multifaceted. The increasing penetration of internet access, coupled with the rising cost of traditional healthcare, has created a demand for more affordable and accessible alternatives. Furthermore, the aging global population and the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases further necessitate innovative solutions for managing healthcare needs. The healthcare industry itself is recognizing the potential of telemedicine to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance patient outcomes.
AI Integration: The Game Changer
While telemedicine is already making waves, the integration of AI is poised to exponentially amplify its impact. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data generated through telemedicine platforms, identifying patterns, predicting health risks, and personalizing treatment plans. This allows for proactive interventions, earlier diagnoses, and improved disease management.
Here are some key ways AI is impacting telehealth:
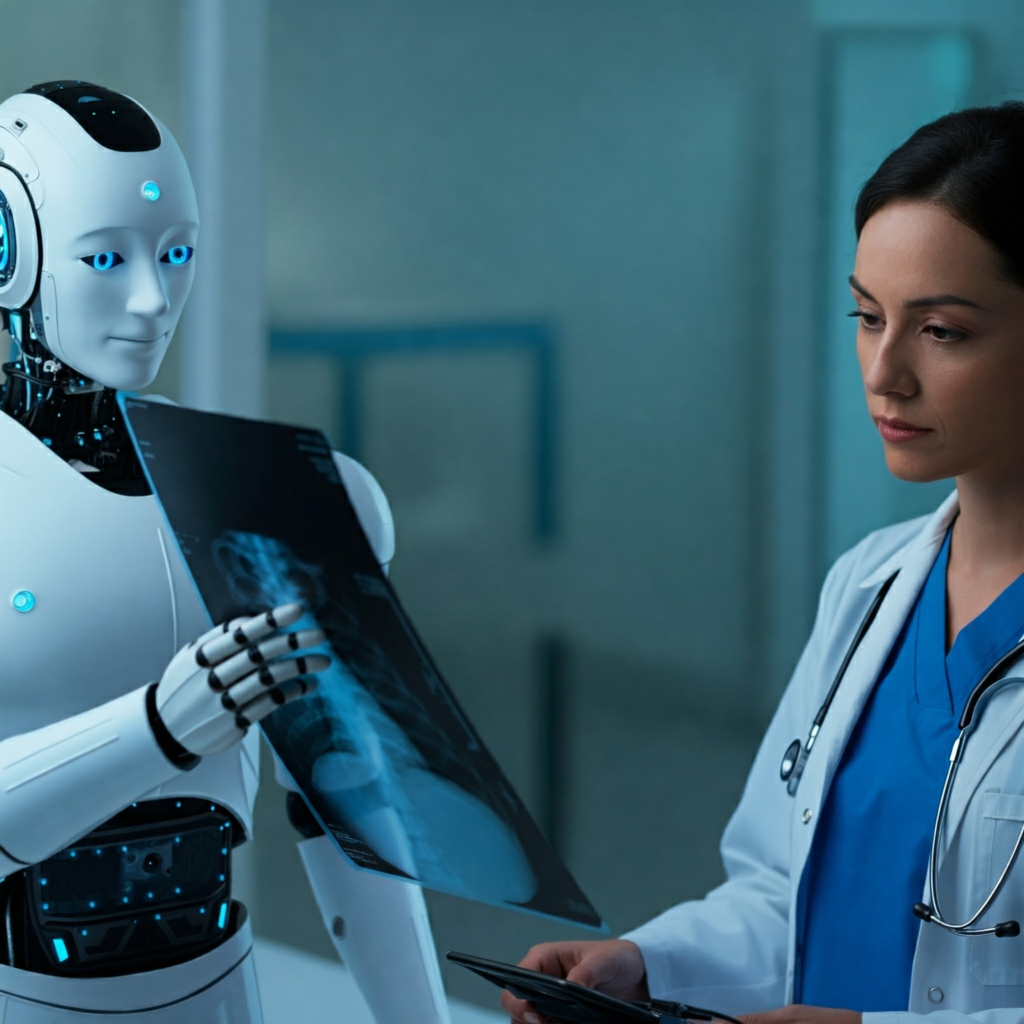
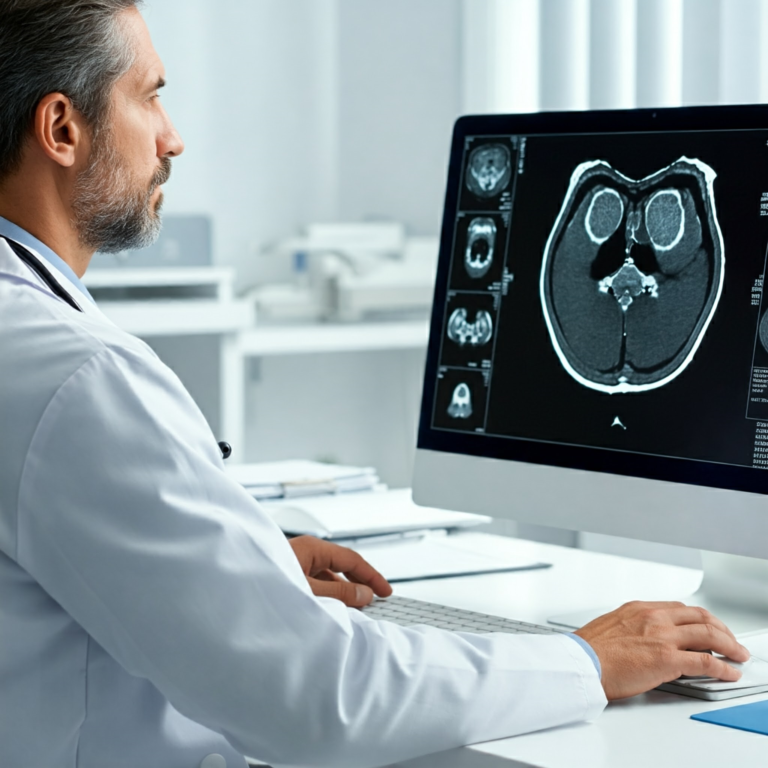
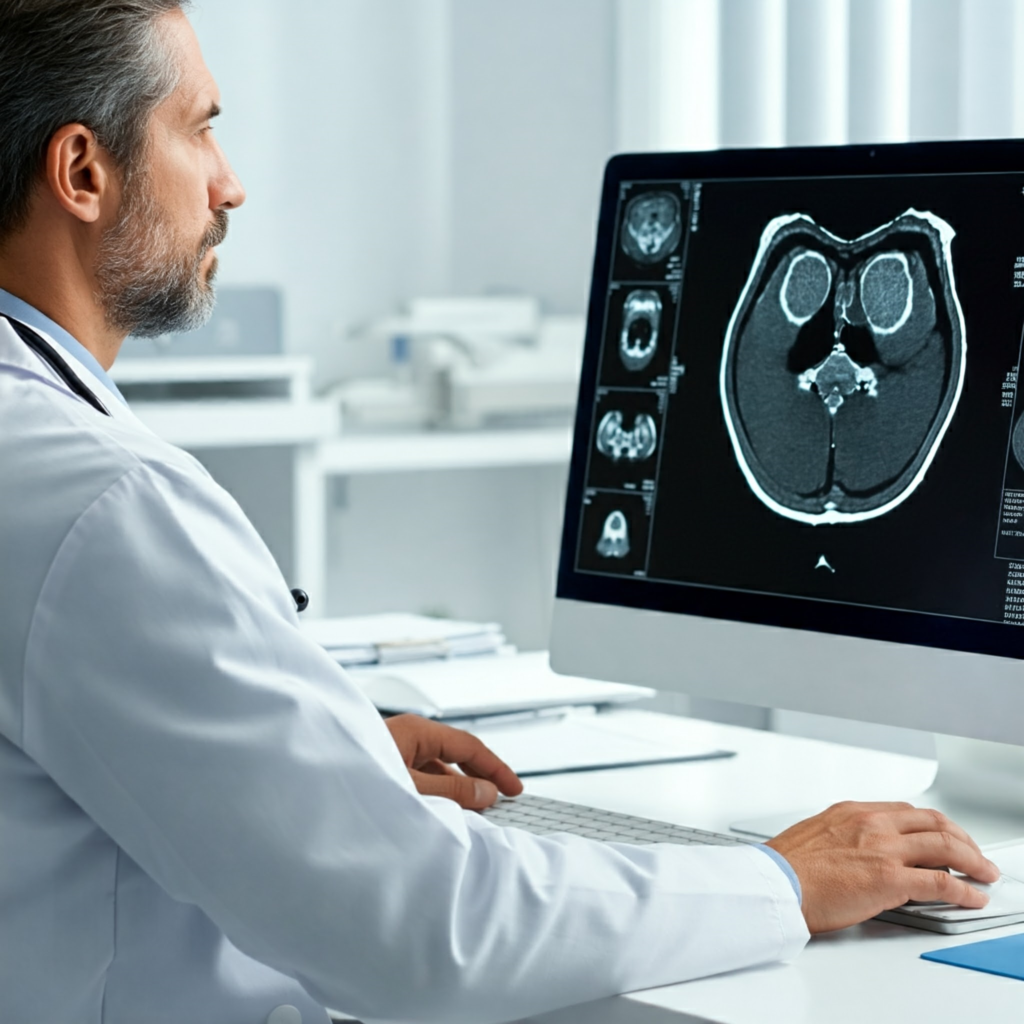
- Enhanced Diagnostics: AI-powered image recognition software can analyze medical images (X-rays, CT scans, etc.) remotely, aiding in quicker and potentially more accurate diagnoses. This is especially beneficial in specialties like radiology and pathology.
- Personalized Treatment: AI algorithms can analyze patient data, including medical history, lifestyle factors, and genetic information, to develop personalized treatment plans. This allows for targeted interventions tailored to individual needs.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: AI-powered wearable devices and sensors can collect real-time patient data, such as vital signs, activity levels, and sleep patterns. This continuous monitoring allows for proactive intervention and early detection of potential health issues.
- Virtual Assistants and Chatbots: AI-powered virtual assistants can provide patients with 24/7 access to information, answer basic medical questions, schedule appointments, and provide medication reminders. This reduces the burden on healthcare providers and improves patient engagement.
- Drug Discovery and Development: AI is accelerating drug discovery and development by analyzing complex biological data and identifying potential drug candidates. This has significant implications for the future of pharmaceuticals and personalized medicine.
Key Trends and Statistics
The convergence of AI and telehealth is generating a flurry of activity in the market. Some key trends to watch include:
- Increased Investment: Venture capital funding in AI-powered telehealth companies is surging, indicating strong market confidence in the sector’s potential.
- Strategic Partnerships: Healthcare providers, technology companies, and pharmaceutical giants are forming strategic alliances to develop and deploy AI-driven telehealth solutions.
- Regulatory Developments: Governments and regulatory bodies are beginning to grapple with the implications of AI in healthcare, working to establish guidelines and standards for its safe and ethical use.
(Note: Due to the article being written in 2000, precise market statistics would be outdated and inaccurate. Instead, focus on the general trends and expectations at the time. Mention the growth of internet access and mobile phone usage as key indicators of the telehealth market’s potential. You could also refer to the increasing interest in online health information seeking and the growing adoption of electronic health records by healthcare providers.)
Recent Market News (Simulated for Year 2000):
- "[Fictional Company A] secures funding for its AI-powered remote patient monitoring platform targeting heart failure patients."
- "[Fictional Hospital B] announces a pilot program using AI-assisted diagnostic tools in its tele-radiology department."
- "[Fictional Tech Company C] partners with a leading pharmaceutical company to develop AI algorithms for personalized drug delivery."
The Future of Remote Care: Promise and Peril
The future of remote care is inextricably linked to the development and deployment of AI in telehealth. The potential benefits are immense, offering the promise of improved access, enhanced quality, and increased efficiency in healthcare delivery. However, along with the promise comes peril. Ethical considerations surrounding data privacy, algorithm bias, and the potential displacement of healthcare professionals need careful consideration.
The successful integration of AI in telehealth requires a collaborative approach involving stakeholders across the healthcare ecosystem. This includes healthcare providers, technology developers, regulators, and patients. Open dialogue, rigorous testing, and ongoing evaluation are crucial to ensuring that AI is used responsibly and ethically to enhance, not replace, the human element in healthcare.
Furthermore, addressing the digital divide is essential to ensure equitable access to the benefits of AI-powered telehealth. Initiatives aimed at increasing internet access and digital literacy are crucial to prevent exacerbating existing health disparities.
Ultimately, the future of remote care hinges on our ability to harness the power of AI while mitigating its risks. By prioritizing patient well-being, promoting transparency, and fostering collaboration, we can unlock the transformative potential of AI to create a healthier and more equitable future for all.