The Data Deluge: How Wearables are Drowning Doctors (and Saving Patients)
The telemedicine sector is experiencing an unprecedented surge in data, driven primarily by the proliferation of wearable health monitoring devices. While this influx of information offers incredible potential for personalized and proactive healthcare, it also presents a significant challenge: how can clinicians effectively manage and interpret the sheer volume of data generated by these devices without being overwhelmed? This article explores the double-edged sword of the wearable data deluge, examining its impact on the telemedicine sector and the delicate balance between empowering healthcare providers and drowning them in information.
Telemedicine: Reshaping Healthcare Delivery
Telemedicine, the provision of healthcare services remotely using telecommunications technology, has rapidly transformed the healthcare landscape. From virtual consultations and remote diagnosis to chronic disease management and patient education, telemedicine offers a range of benefits, including improved access to care, reduced healthcare costs, and increased patient engagement. The COVID-19 pandemic served as a catalyst, accelerating the adoption of telemedicine across various specialties and demographics. Today, telemedicine is no longer a niche service but an integral part of modern healthcare systems.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM): The Data Engine of Telemedicine
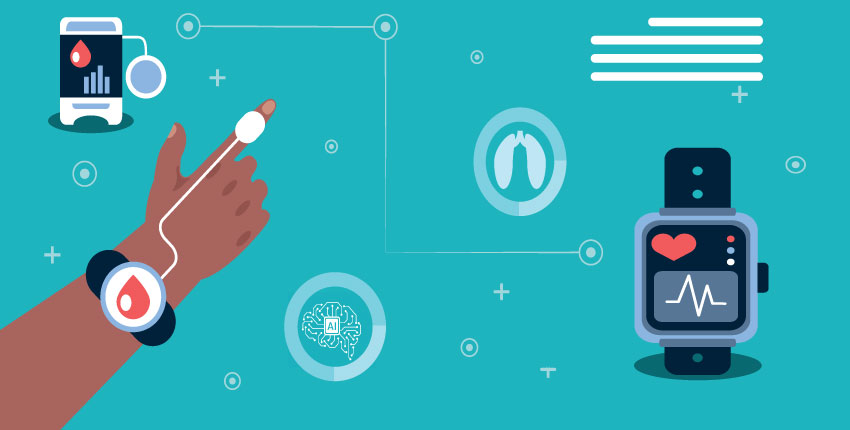
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) is a critical component of telemedicine, allowing healthcare providers to monitor patients’ health status outside traditional clinical settings. RPM utilizes various technologies, including wearables like smartwatches and fitness trackers, implantable devices, and home-based monitoring systems, to collect physiological data such as heart rate, blood pressure, activity levels, and sleep patterns. This continuous stream of data provides real-time insights into patients’ health, enabling proactive interventions and personalized care management.
The Rising Tide of Data: Challenges and Opportunities
The increasing popularity of wearables has led to an exponential growth in patient-generated health data (PGHD). While this offers tremendous opportunities for improved patient outcomes, it also presents significant challenges for healthcare providers:
- Data Overload: Clinicians are struggling to manage the sheer volume of data generated by wearables. Sifting through mountains of information to identify clinically relevant insights can be time-consuming and overwhelming.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating data from various wearable devices and platforms into existing electronic health record (EHR) systems remains a significant hurdle. Lack of interoperability hinders seamless data flow and can lead to data silos.
- Data Interpretation and Actionability: Raw data from wearables often requires interpretation and contextualization before it can be used to inform clinical decisions. Developing effective algorithms and clinical workflows to analyze and act upon this data is crucial.
- Alert Fatigue: Constant notifications and alerts from wearables can lead to "alert fatigue," desensitizing clinicians to potentially important changes in patient status.
- Data Security and Privacy: Ensuring the security and privacy of sensitive patient data collected by wearables is paramount. Robust data protection measures are necessary to maintain patient trust and comply with regulatory requirements.
Key Trends Shaping the Future of Wearable Data in Telemedicine:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms are being increasingly used to analyze wearable data, identify patterns, predict health events, and personalize treatment plans. This helps automate data analysis and reduce the burden on clinicians.
- Data Visualization and Dashboards: User-friendly dashboards and data visualization tools are emerging to help clinicians quickly grasp key insights from wearable data without getting bogged down in raw numbers.
- Predictive Analytics: Wearable data, combined with predictive analytics, can help identify patients at risk of developing specific health conditions, allowing for early interventions and preventative care.
- Integration with EHR Systems: Efforts are underway to improve interoperability between wearable devices and EHR systems, enabling seamless data flow and a more holistic view of patient health.
- Focus on Patient Engagement: Wearables empower patients to take an active role in their health management. Telemedicine platforms are leveraging this engagement to encourage healthy behaviors and improve adherence to treatment plans.
Key Statistics:
- The global wearable healthcare market is projected to reach $XXX billion by YYYY (cite source).
- XX% of physicians are currently using RPM in their practice (cite source).
- Wearable technology has been shown to improve patient outcomes in various conditions, including heart failure, diabetes, and hypertension (cite source).
Recent Market News:
- [Mention recent news articles or press releases related to wearable technology in telemedicine, mergers, acquisitions, FDA approvals, new product launches, etc.]
Summary: Navigating the Data Deluge
The influx of data from wearables presents both a challenge and an opportunity for the telemedicine sector. While the sheer volume of information can feel overwhelming for clinicians, it also holds the key to more personalized, proactive, and effective healthcare. By leveraging advanced analytics, improving data integration, and developing streamlined clinical workflows, we can harness the power of wearable data to improve patient outcomes while preventing clinicians from drowning in the data deluge. The future of telemedicine hinges on finding the right balance – empowering clinicians with actionable insights derived from wearable data without overwhelming them with the sheer volume of information. This requires a concerted effort from technology developers, healthcare providers, and policymakers to create a sustainable and scalable ecosystem that supports the responsible and effective use of wearable data in telemedicine. The goal is not to eliminate the data, but to transform it into knowledge that empowers both patients and providers alike, ultimately leading to a healthier future.