Telemedicine’s AI Takeover: Hype or Healthcare Revolution?
(Date: October 26, 2000)
The burgeoning field of telemedicine, once a futuristic concept relegated to science fiction, is rapidly transforming the healthcare landscape. No longer confined to pilot programs and niche applications, telemedicine is steadily gaining acceptance among patients and providers, promising increased access, improved efficiency, and potentially lower costs. But the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into this evolving field raises a crucial question: Is it merely hype, or are we witnessing the dawn of a true healthcare revolution?
Telemedicine: Reshaping Healthcare Delivery
At its core, telemedicine encompasses the use of telecommunications technologies to provide remote clinical services. From video conferencing consultations and remote patient monitoring to electronic transmission of medical images and data, telemedicine bridges geographical barriers, connecting patients with specialists they might otherwise never reach. In 2000, this holds particular significance for rural communities and underserved populations facing limited access to healthcare facilities.
The driving forces behind telemedicine’s growth are multifaceted. Rising healthcare costs, an aging population with increasing healthcare needs, and a shortage of healthcare professionals, particularly in specialized fields, all contribute to the demand for innovative solutions. Telemedicine offers a compelling answer, potentially reducing the burden on traditional healthcare systems while simultaneously extending their reach.
Within the broader healthcare industry, telemedicine is carving out a distinct niche. Initially perceived as a supplementary service, it is increasingly recognized as an integral component of comprehensive healthcare delivery. This shift in perception is driven by several factors, including advancements in technology, growing evidence of its effectiveness, and increasing acceptance by both patients and providers.
The AI Infusion: Transforming Telemedicine
The integration of AI into telemedicine represents a paradigm shift, promising to elevate the field beyond simple remote consultations. AI algorithms are being deployed in various capacities, enhancing diagnostic accuracy, personalizing treatment plans, and automating administrative tasks.
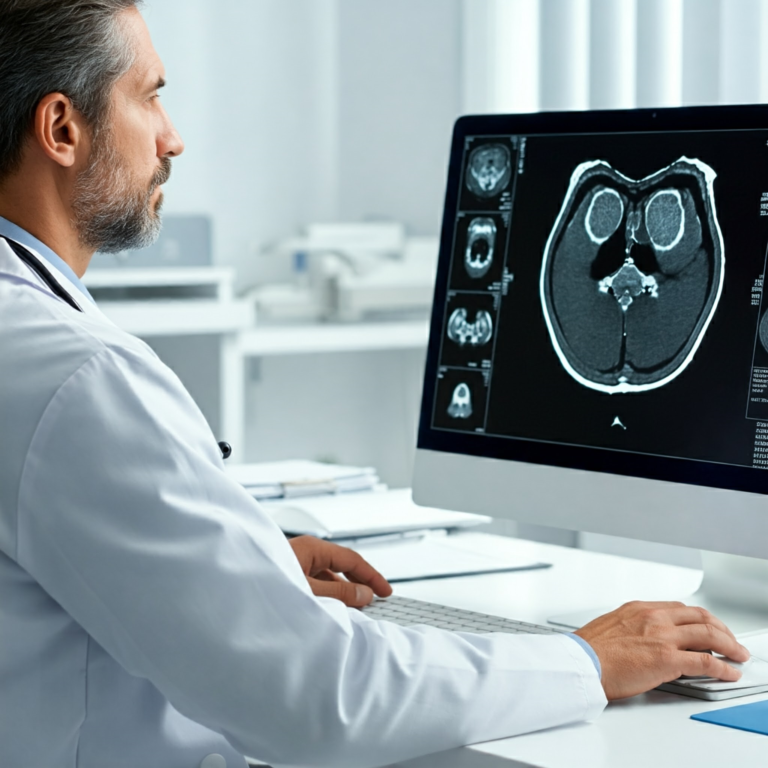
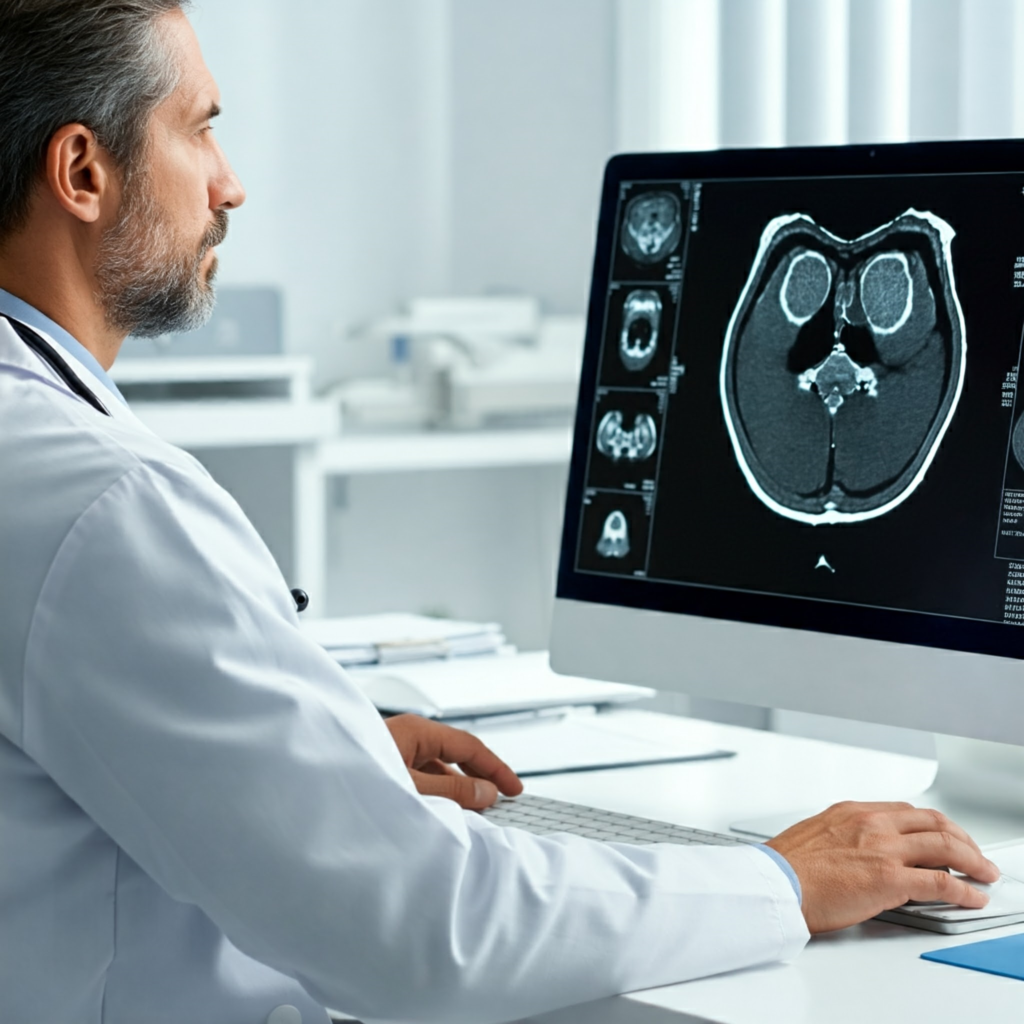
One of the most promising applications of AI in telemedicine lies in diagnostic imaging. AI-powered image analysis tools can detect subtle anomalies often missed by the human eye, leading to earlier and more accurate diagnoses. This is particularly valuable in fields like radiology and pathology, where rapid and precise interpretation of images is crucial.
Furthermore, AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of patient data, identifying patterns and predicting health risks. This predictive capability enables proactive interventions, potentially preventing the onset of chronic diseases and reducing the need for costly hospitalizations.
Beyond diagnostics, AI is transforming the patient experience in telemedicine. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide 24/7 access to basic medical information, answer patient queries, and schedule appointments, freeing up human resources for more complex tasks.
Key Trends Shaping the Future
- Increased adoption of wearable technology: Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, generate a continuous stream of patient data, offering valuable insights into individual health patterns. AI algorithms can analyze this data to personalize treatment plans and monitor patient progress remotely.
- Expansion of remote patient monitoring: Chronic diseases, such as diabetes and heart failure, require ongoing monitoring. Telemedicine, coupled with AI-powered remote monitoring systems, allows healthcare providers to track vital signs, medication adherence, and other crucial data, enabling timely interventions and preventing hospital readmissions.
- Growing emphasis on data security and privacy: As telemedicine becomes more reliant on data transmission, concerns about data security and patient privacy are paramount. Robust security measures and strict adherence to privacy regulations are crucial for building trust and ensuring the long-term success of telemedicine.
Key Statistics (Projected for 2000-2005)
- The global telemedicine market is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 20% during this period.
- North America is expected to dominate the market, driven by high healthcare spending and increasing adoption of advanced technologies.
- Significant investments are being made in telemedicine infrastructure and research, indicating a strong belief in the future of the field.
Recent Market News
- Several major healthcare providers are partnering with technology companies to develop and implement telemedicine solutions.
- Government agencies are increasingly recognizing the potential of telemedicine to improve healthcare access and affordability.
- New regulations and reimbursement policies are being developed to support the growth of the telemedicine sector.
Summary: Hype or Revolution?
The integration of AI into telemedicine is undeniably transforming the healthcare landscape. While the term "takeover" might seem dramatic, the impact of AI is undeniable, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in remote healthcare delivery. Beyond the hype, the tangible benefits of AI-powered telemedicine are becoming increasingly apparent. Improved diagnostic accuracy, personalized treatment plans, increased efficiency, and enhanced patient access represent a significant step towards a more accessible, affordable, and effective healthcare system. Challenges remain, particularly in areas like data security, regulatory frameworks, and ensuring equitable access to technology. However, the trajectory is clear: AI and telemedicine are converging to create a genuine healthcare revolution, one that promises to reshape the future of medicine.